A Nuclear Renaissance? New Power Plants Emerge in a Changing Energy Landscape
The world’s energy landscape is in constant flux, driven by the twin imperatives of climate change mitigation and energy security. Amidst the rapid rise of renewables like solar and wind, a surprising trend is emerging: the construction of new nuclear power plants. While the industry faced a period of decline in the late 20th century, a renewed interest in nuclear energy is taking shape, driven by a confluence of factors.
This article delves into the reasons behind this nuclear renaissance, exploring the new generation of reactors, the challenges they face, and the potential impact on the global energy mix.
The Case for Nuclear: A Clean and Reliable Energy Source
Nuclear power has long been touted as a clean and reliable source of energy, offering several advantages over fossil fuels:
- Low Carbon Emissions: Nuclear power plants generate electricity with minimal greenhouse gas emissions, making them a key player in the fight against climate change.
- High Energy Density: Nuclear fuel has an incredibly high energy density, requiring significantly less fuel than fossil fuels to generate the same amount of power. This translates to less waste and a smaller environmental footprint.
- Baseload Power: Nuclear power plants provide a consistent and reliable source of electricity, operating 24/7 regardless of weather conditions. This makes them ideal for meeting baseload demand, ensuring a stable power grid.
- Job Creation: The construction and operation of nuclear power plants create significant employment opportunities, contributing to economic development.
The Challenges of Nuclear: Safety, Waste, and Cost
Despite its advantages, nuclear power has historically faced several challenges, including:
- Safety Concerns: The accidents at Chernobyl and Fukushima raised public concerns about the safety of nuclear power, leading to a decline in its popularity.
- Nuclear Waste Disposal: The safe and permanent disposal of nuclear waste remains a major challenge. Finding suitable storage facilities and ensuring long-term safety is a complex and expensive undertaking.
- High Construction Costs: Nuclear power plants are expensive to build, with construction times often exceeding initial estimates. This has deterred many investors and governments from pursuing new projects.
- Proliferation Concerns: The use of nuclear technology raises concerns about the potential for nuclear weapons proliferation. International regulations and safeguards are crucial to mitigating this risk.
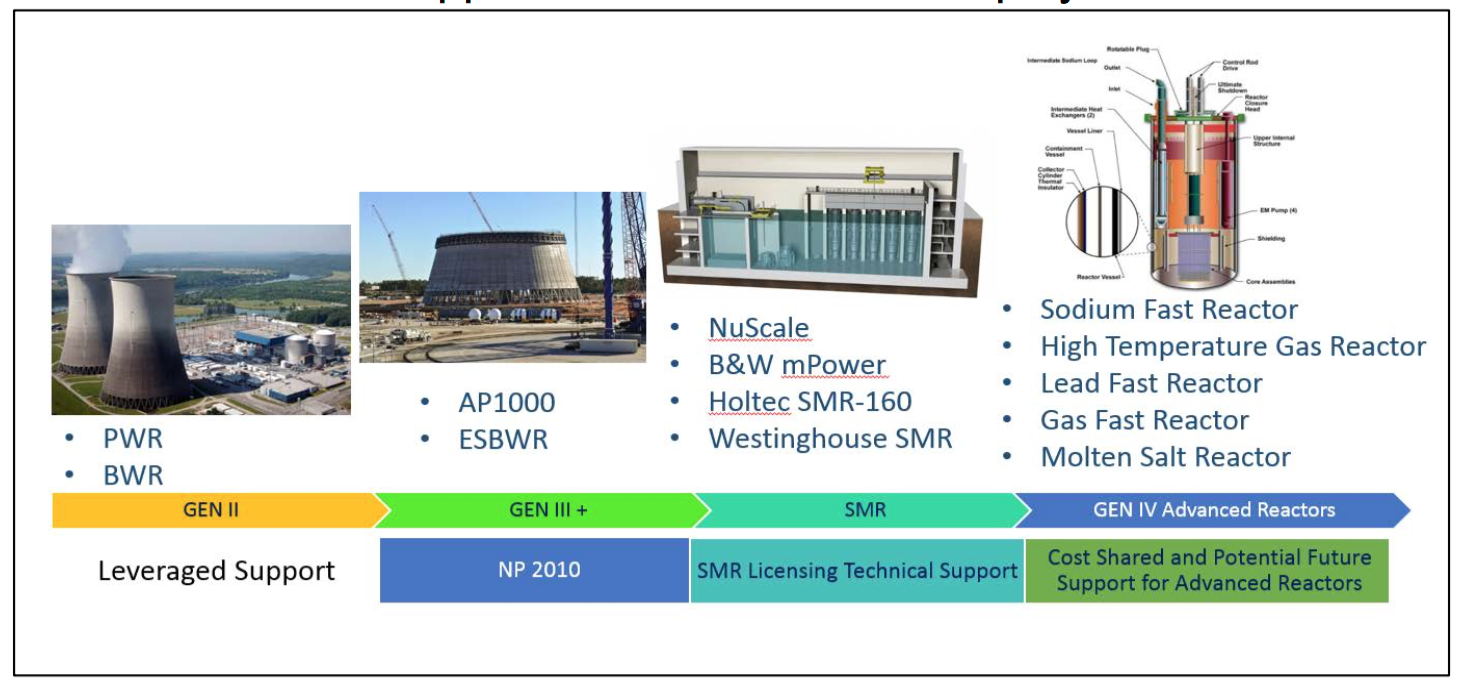
The Rise of New Reactor Technologies: Addressing Past Concerns
The new generation of nuclear reactors addresses many of the concerns raised by the older designs. These advanced reactors offer improvements in safety, efficiency, and waste management, making them more attractive to investors and governments.
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): These reactors are smaller and more modular than traditional designs, making them easier and faster to build and deploy. They also offer enhanced safety features, including passive safety systems that operate without human intervention.
- Fast Neutron Reactors: These reactors can use nuclear waste as fuel, reducing the need for long-term storage and potentially offering a solution to the waste disposal problem.
- Molten Salt Reactors (MSRs): These reactors use liquid salt as a coolant, offering improved safety and efficiency. They also have the potential to produce hydrogen, a clean energy source.
A Global Nuclear Revival: New Plants Under Construction
Despite the challenges, the world is witnessing a resurgence in nuclear power. Several countries are actively pursuing new nuclear projects, driven by a combination of factors, including:
- Climate Change Targets: Many countries have set ambitious climate change targets, making nuclear power a critical tool for achieving carbon neutrality.
- Energy Security: The geopolitical instability and energy crisis have highlighted the need for reliable and domestically sourced energy, making nuclear power more attractive.
- Technological Advancements: The development of new reactor technologies has addressed many of the concerns surrounding traditional nuclear power, making it more appealing to investors and governments.
The United States: A Mixed Bag of Progress and Challenges
The United States, once a leader in nuclear power, has seen a decline in its nuclear fleet in recent years. However, the country is experiencing a renewed interest in the technology, with several new projects in the planning and development stages.
- Small Modular Reactors (SMRs): The US Department of Energy is actively supporting the development and deployment of SMRs, with several companies working on commercial projects.
- Existing Reactors: Several existing nuclear power plants are receiving upgrades and extensions, extending their operational lifespan and ensuring a continued source of clean energy.
- Challenges: Despite the renewed interest, the US faces challenges in securing financing, navigating regulatory hurdles, and addressing public concerns.
China: A Nuclear Powerhouse
China has emerged as a global leader in nuclear power, aggressively expanding its nuclear fleet. The country is building numerous new reactors, including both traditional designs and advanced technologies.
- Ambitious Expansion: China has set ambitious targets for nuclear power expansion, aiming to significantly increase its nuclear capacity in the coming years.
- Domestic Technology: China is developing its own nuclear technology, including SMRs and fast neutron reactors, reducing its reliance on foreign suppliers.
- Challenges: China faces challenges in managing the safety of its growing nuclear fleet and ensuring the responsible disposal of nuclear waste.
Europe: A Balancing Act of Sustainability and Security
Europe is facing a complex energy landscape, grappling with the need to reduce reliance on Russian gas while maintaining energy security. Nuclear power is playing a significant role in this transition.
- Renewed Interest: Several European countries, including France, Germany, and the UK, are re-evaluating their nuclear power policies, recognizing its potential to contribute to energy security and climate change mitigation.
- Existing Reactors: Many European countries are extending the operating lives of existing reactors, providing a bridge to a future with more renewables and advanced nuclear technologies.
- Challenges: Europe faces challenges in financing new nuclear projects, managing public opinion, and ensuring the safe disposal of nuclear waste.
The Future of Nuclear: A Critical Role in a Clean Energy Future
While nuclear power faces challenges, its potential to contribute to a clean energy future cannot be ignored. As the world strives to achieve carbon neutrality, nuclear power offers a reliable and low-carbon energy source that can complement renewable energy sources.
- Bridging the Gap: Nuclear power can provide baseload power, ensuring a stable electricity supply even when renewable energy sources like solar and wind are intermittent.
- Addressing Climate Change: Nuclear power plays a crucial role in reducing greenhouse gas emissions, helping to mitigate the impacts of climate change.
- Technological Advancements: The development of new reactor technologies, including SMRs and fast neutron reactors, is making nuclear power more attractive and addressing past concerns.
Conclusion: A Balanced Approach
The future of nuclear power is not without its complexities. It is crucial to acknowledge the challenges while recognizing the technology’s potential to contribute to a clean energy future. A balanced approach that considers the safety, cost, and waste management challenges while harnessing the benefits of nuclear power is essential.
As the world transitions to a cleaner and more sustainable energy system, nuclear power will likely play a significant role, alongside renewable energy sources. By addressing the challenges and embracing innovation, nuclear energy can contribute to a future with cleaner air, a stable energy grid, and a more sustainable planet.